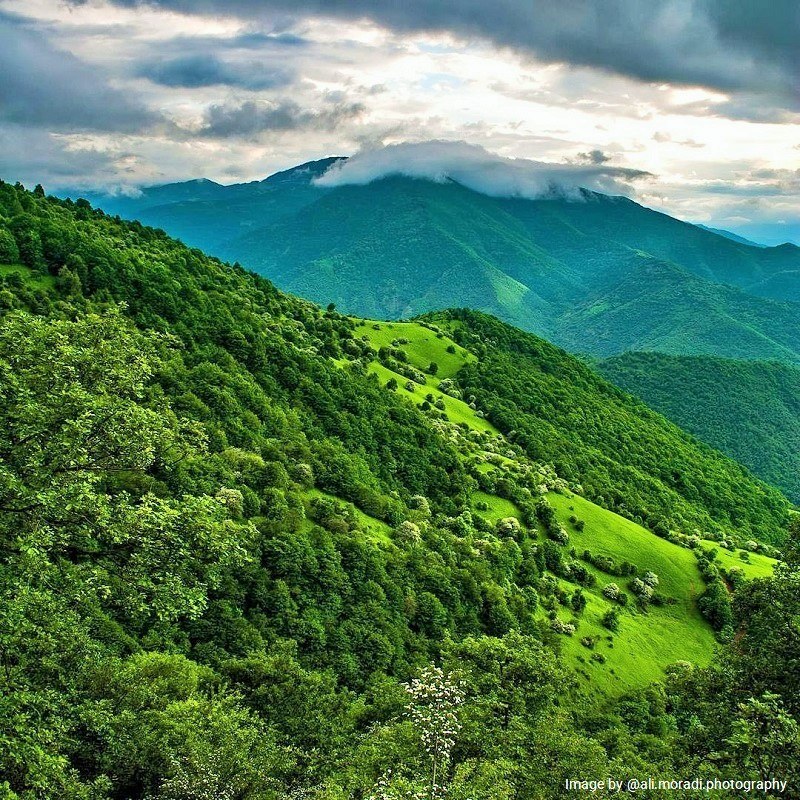
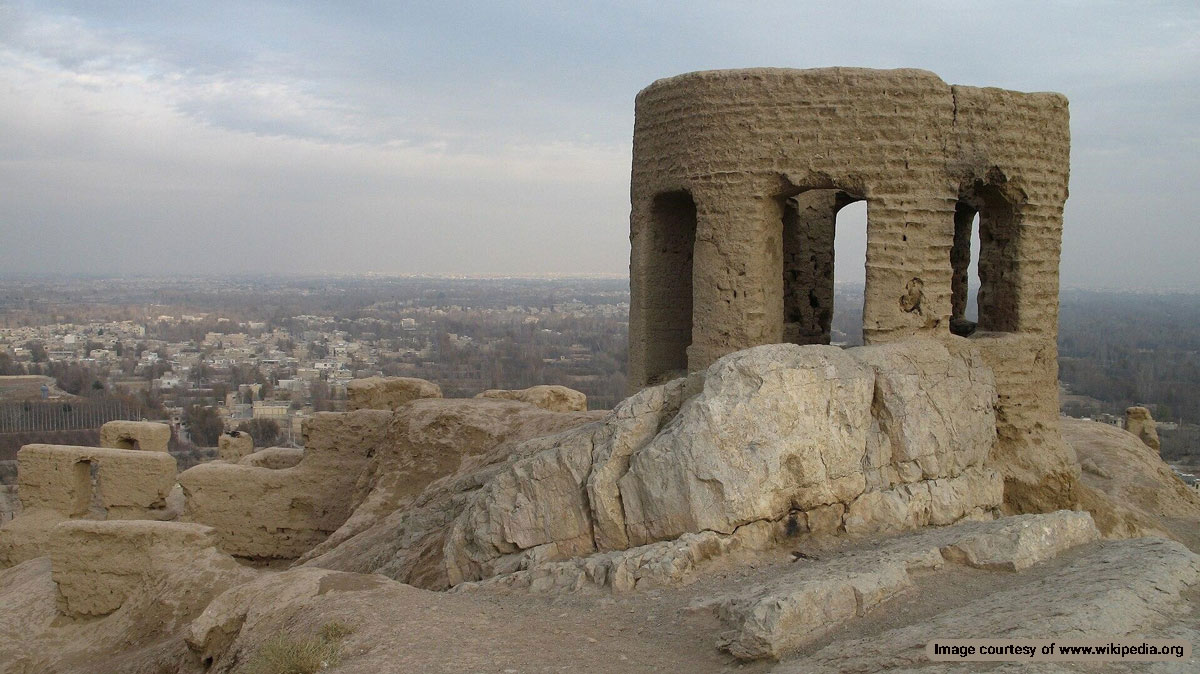
There are areas in the world called the biosphere reserve. These areas are internationally protected bio-natural areas. UNESCO has covered these protected areas under Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB). Arasbaran biosphere reserve in Iran is one of these protected areas. There are 107 biosphere reserves worldwide. Iran has got more than a dozen of them.
Introducing Arasbaran Biosphere Reserve of Iran
Arasbaran region is located in the north of East Azerbaijan Province. This is a mountainous area. The other name of Arasbaran is Qara Dag. The region is located between the Caspian, Caucasian, and Mediterranean regions and is close to the Iranian border with the Republic of Azerbaijan and Armenia. The area is approximately 125,255 hectares.
Arasbaran biosphere reserve is a mountainous region with altitudes varying from 256 meters to 2,896 meters above sea level. In some parts of the area, there are mountains up to 2,201 meters high. It also includes a wide variety of grasslands, semi-arid plains, ranges and forests, rivers, and springs. Many rivulets originate from the high mountains of Arasbaran. Eventually, these rivulets enter the Aras River.

There are about 2400 species of plants identified in Azerbaijan. About 1400 species of them live in the Arasbaran forests. There are also more than 250 species of fungi in the area. We can find more than 1,000 plant species in the area survived since the Ice Age.
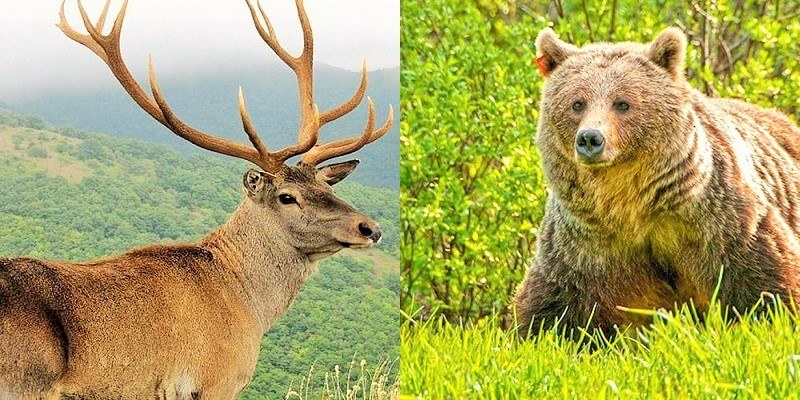

There are also many fossils in this area. The red deer is one of the mammals in the Arasbaran region.
According to the researchers, three points in Arasbaran are the major tourist attraction:
- Babak Castle
- Makidi Valley
- Aynalou
The three sites are located near Kaleybar-Asheqlou Road (Abbas Abad-Aynalou-Wayqan Road). The mausoleum of Baba Seifuddin near the Garmanab Village is also a religious place of interest for the nomads of Arasbaran.
In addition to their natural beauty, the numerous summer highland pastures (yaylaq) in Arasbaran are a great opportunity to see the nomad culture. The following are some good examples of the yaylaqs:
- Bastamloo Tribes yaylaq in the pastures between Shoja Abad Village and Babak Castle (Baz Castle)
- The mountains of Aliabad village (Kaleybar), Chaparli and Aqdash
- Motalli Village
The Arasbaran biosphere is influenced by the Mediterranean climate. Due to the high altitude difference, it enjoys a variety of climates. Kaleybar is the closest residential area to Arasbaran. The average annual precipitation at the Kaleybar weather station during a period of 20 years was 461 mm. Precipitation in this area is relatively high and it snows most of the time.
The appearance and distribution of the vegetation in the Arasbaran biosphere reserve area have a specific regulation:
- The southern foothills are covered with grass fields;
- In the northern foothills, there are mainly forests between the altitudes of 800 meters and 2200 meters;
- The areas of more than 2200 m high and less than 800 m high are meadows.
There are 220 bird species, 38 reptile species, 5 amphibian species, 48 mammal species, and 22 fish species.
Arasbaran hot springs are one of the tourist attractions of this region. Kaleybar Hot Spring is the largest water treatment complex in Iran.
Anthropology of Arasbaran Biosphere Reserve
Qarabaq tribe or Arasbaran tribe is one of the oldest tribes in the country. There are six separate tribes with a population of over 1,330 members in the area. There are also 66 villages with a total population of 11,192. 14,322 inhabitants of these 66 villages live in the Arasbaran biosphere reserve. The main activities of the people include agriculture, horticulture, bee production, and livestock production.
Major Historical Monument in Arasbaran Area
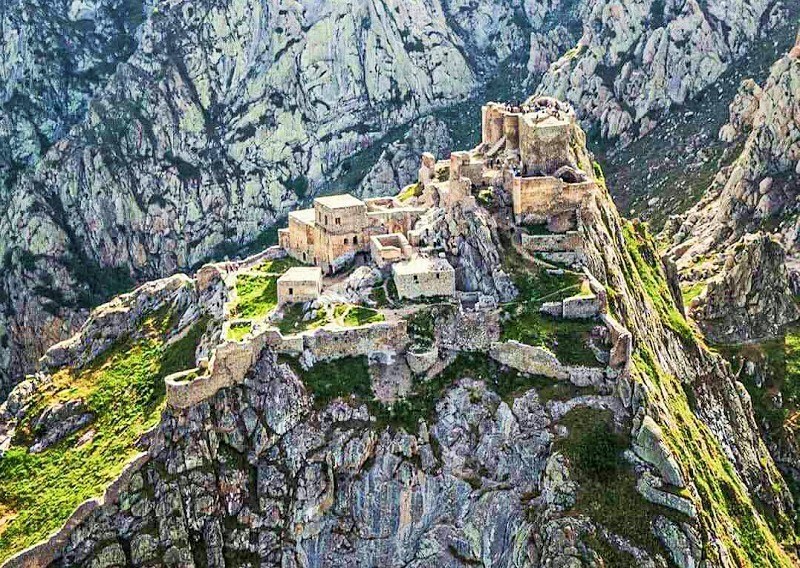

The most outstanding monuments are:
Kaleybar Castle (Babak Castle, Jomhour Castle or Baz Castle)
Archaeologists attribute the construction of this castle to the Sassanid period. The castle was a command center of Babak Khoramdin, one of the main Iranian nationalist revolutionaries resisting the Arab invaders of the 7th century. Kaleybar Castle is located near Kaleybar City.
Peygham Castle
The building is located 10 kilometers south of Kaleybar and near Payam Village. This castle is located on a mountain and there is Kaleybar River under the castle. There are few remnants of the building and the walls of the monument. The castle dates back to the Parthian period. It was through this monument that the watchmen guarded the entrance to the historical city of Bar, or Kaleybar.
Pashtou Castle (Poshtab Fortress)
It is located at the highest point of a mountain between Poshtab and Kojan village. The height of the mount is more than 3000 meters above sea level. The historical role of these castles and military sites has been to combat the invaders.
Avarsin Castle
It is one of the historical castles in Avarsin Village.
Kaleybar Friday Mosque
The monument has a large dome. It also had a 5-meter-high minaret destroyed in the past during the Russians’ bombardment.
Shah Qasem Tomb
The tomb is located 50 kilometers from Kaleybar County. Local people believe that the tomb belongs to the brother of Imam Reza who came to this region to spread Islam.
Hamam-e Qadimi (Old Bath)
Only small domes, once used as bath lights, have remained from this old bath. People used this bath there until approximately half a century ago.
Natural Attractions of Arasbaran Biosphere Reserve
There are many landmarks in the Arasbaran area. Here are some examples:
- Kavanaq Old Planetree: this tree is completely in good health. The tree is about three meters in diameter. It is located at the entrance of Kavanaq Village. This tree is more than 500 years old and has a special place in the rituals of the villagers and nomads.
- Cedar Tree of the Cemetery of Sowme’eh Village: this old tree has twisted forms on all parts of its trunk, even on the small branches. It is distinct from other cedar trees in the area and cemetery;
- Old oak tree in Chariq Village;
- Old plane trees Shah Heydar, Makidi, and Toali Sofla villages.
Culture of Arasbaran Nomads
Arasbaran biosphere reserve is the residence of about 23,500 nomads. There are different economic activities in this area such as agriculture, animal husbandry, horticulture, handicrafts, and tourism. The spoken language of the local people is Azeri. The majority of the people are Shiite.
Until the early twentieth century, a substantial Christian population lived in the villages of Arasbaran biosphere reserve. However, few Christians live in this area now.
The cultural identity of the people of this region has gradually shifted to oral culture. By oral culture, we mean there is oral communication (listening and speaking) without recording. Two factors have played a decisive role in the overall direction of this issue.
- Lack of spoken language (Azeri) while it is an official language (Persian) and written.
- Due to the specific structure of the Azeri language, the boundary between individual memories and collective memories is blurred -a feature that makes it very easy to create an oral culture in different forms.
As a result, collecting and writing the culture of the Arasbaran area has not been customary. The poetry book of Mohammad Golmohammadi entitled Qara Dag and the book of Abbas Barez entitle El Daiaqina Salam are two books that partly reflect the culture and customs of the nomads of Arasbaran.
As migrating nomads cross this Arasbaran biosphere reserve, there is a unique style of music. It has also led to the development of a kind of music called Ashiq. The music and songs developed as such are related to nature. On the other hand, the themes of the Ashiq songs are about nomads’ migration and their feelings.
History of the Region

Eight hundred years ago, famous writers such as Yaqut al-Hamawi wrote about Kaleybar and Ahar (cities near Arasbaran). The two cities were thriving before the Ilkhanid period.
In the Safavid era, Iranians paid particular attention to Ahar City. The Safavid kings attempted to introduce Azerbaijan as the origin and the base of their dynasty.
During the Qajar period, Arasbaran was the center of royal attention. The nomads of Arasbaran constituted most of the Iranian warriors against the Russian Army.
In addition, Arasbaran was one of the bases of the Iranian constitutional movement. At the time of the First Pahlavi king, most of the nomads chose to settle in one place. Since then, the region changed into a calm area.
Comparison with Similar Areas
Now, we will have a quick look at the other areas that are similar to the Arasbaran biosphere reserve.
Arzhan Lake
Arzhan is one of the southern lakes of Iran. This area is located in the Arzhan plain in Fars Province. It is 60 km away from Shiraz and is adjacent to the main road of Shiraz-Kazeroon.
The lake is about two thousand hectares and is a freshwater lake. The area is located near the historical monuments of Bishapur and Shapur Cave. Arzhan Region is a protected area as a biosphere reserve. This lake is a habitat for migratory birds.
Famur Lake (Parishan or Moor)
It is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Iran and the Middle East, approximately 4300 hectares, which dates back to millions of years ago. It has a height of 820 meters above sea level.
Famur is a protected area located near Kazeroon City. It is one of the stable ecosystems created by tectonic factors.
Geno Protected Area
This protected area, with an area of 43000 hectares, is one of the UNESCO Biosphere Reserves in Iran. It is located northwest of Bandar Abbas. It is situated in a pleasant climate and relatively surrounded by mountains. The most important human activities in this area include animal husbandry, agriculture, ecotourism, and environmental education.
Kavir National Park
Most of this area belongs to the Garmsar City of Semnan Province. A few parts of this park are also located in Tehran, Qom, and Isfahan provinces. The area covers an area of about 670,000 hectares (6700 km2) of which 420,000 hectares are the national park and 250,000 hectares are protected areas.
The wildlife of this area is varied. It used to be known as “Little Africa” and “Serengeti” of Iran. Kavir National Park is the only national park in Iran with no human, mineral and grazing habitat. In total, experts have identified 34 species of mammals, 155 species of birds, and 34 species of reptiles in this area. It is also inscribed in the UNESCO’s list like Arasbaran biosphere reserve.
Mangrove Protected Area and Khoor-e-Khooran International Wetland
Mangrove or Avicennia marina is the name of a particular ecosystem in tropical areas. These forests occur as a result of the accumulation of a number of plants and animals on the lowlands of the firth, delta, pond, and seaside. A variety of aquatic, bird, and amphibian species live in the mangrove forest on the southern coast of Iran. Mangrove forests belong to the group of saline forests.
This area is a complex of mangrove (hara in local language) coastal lush forests. These forests are located near Qeshm Island, Bandar-e Pol, Hormoz Island, and Bandar Khamir in Hormozgan Province. They are also one of the UNESCO Biosphere Reserves in Iran.
Mangrove grows in two protected areas of Iran, in the coast of the Persian Gulf and the Oman Gulf. The northern and western coasts of Qeshm Island and the Nayband Forest of Bushehr Province are the most important mangrove forests of Iran.
Lake Urmia (Oromeeh) National Park
This region is located between East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan provinces. The area of the park is 464,056 square meters. The lake has 102 islands, large and small, covering an area of 33,486 hectares. There are a total of 10 waterfalls in Lake Urmia National Park. Lake Urmia is an inscribed UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in Iran.
Miankaleh Peninsula
This peninsula is in the southeast of the Caspian Sea. It is located twelve kilometers north of Behshahr City in Mazandaran Province of Iran. Its area is more than 68,000 hectares and its height is between 15 and 28 meters below international waters level.
Iranians harvest and supply about half of the caviar of Iran from the waters of the area. Currently, UNESCO and the Environmental Protection Organization of Iran protect the wildlife refuge, international wetland, and biosphere reserve of this area. Its natural environment remains relatively untamed.
Dena Mountain Range
The longest and largest fold in the Great Zagros Mountain Ranges is Dena. This local mountain range has a drainage divide of about 90 km long. Mount Dena, called also the Roof of Zagros, is 4,435 meters high, located in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province.
This mountain is one of the 1515 most prominent peaks in the world. Dena starts from 20 kilometers east of Yasuj City and continues to 70 kilometers northwest of this city. It is also one of the UNESCO Biosphere Reserves in Iran.
Tang-e Sayyad
This area is located in Chahar Mahal and Bakhtiari Province. It has an area of about 27,000 hectares. Tang-e Sayad has been inscribed in UNESCO’s list, like Arasbaran biosphere reserves. This area is a suitable habitat for wild ram species due to a large number of hilly terrains.
Hamoon Lake and International Wetland
After Caspian Lake and Urmia Lake, Hamoon is the third largest lake in Iran with an area of 5,660 km2. It is also the 7th international wetland in the world and one of the biosphere reserves in Iran. Hamoon Lake and Wetland are located in Sistan and Baluchestan Province.
It consists of three small lakes joining each other during the abundance of water and forms a common lake between Afghanistan and Iran. The Hirmand River is the main artery entering Hamoon. UNESCO has inscribed the area as a biosphere reserve.
Kopet Daq Mountains
These mountains are located in northern Iran and most parts of it belong to Iran. A small northern part of Kopet Daq is located in southern Turkmenistan. The mountains are formed in the Alpine-Himalayan folds. Their most important features are rich water resources, calcareous constituents, water erosion, and karstic phenomena.
Because of the dominance over the Russian plains, the heights of Kopet Daq were one of the hearts of the earth in the world. The heart of the earth means some parts of the world that have played a key role in conquering a region. It is also one of the UNESCO Biosphere Reserves in Iran.
Golestan National Park or Golestan Forest
This area is located in the east of Golestan Province and west of North Khorasan Province. It is also the oldest registered national park in Iran and a wildlife refuge. There are 1,350 plant species and 302 animal species in the area.
Golestan Park has an area of about 900 km2. UNESCO has inscribed Golestan National Park as a biosphere reserve in the World biosphere reserve list.
Caspian Hyrcanian Mixed Forests
These forests are a biodiversity area on the southern margin of the Caspian Sea. Its area is 55,000 km2. It is also one of the ecosystems of mixed broadleaf forests. The Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests cover some parts of the five northern provinces of Iran. On the other hand, it has share borders between Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan.
It is one of the most valuable forests in the world, dating back to 40 million years ago. People consider the park as the Natural Museum.
This forest is the natural and historical heritage of Iran. Like Arasbaran biosphere reserve, this forest is also inscribed in the UNESCO’s list. Abr Forest of Shahrood is also part of the Hyrcanian forest. The forest is cloudy most of the time.
Dalkhani Forests
This forest is located in Dalkhani Village, 30 kilometers southeast of Ramsar City. The forest is 800 meters above sea level and is located alongside the lush forests of Ramsar. The thick fog covers the forest on most days. It is very cool in summer and cold in winter. Along this forest, 22 km from Ramsar, there is the beautiful village of Javahereh.
Fandoqlu Forests
The forests are located 25 km from Ardebil City. Fandoqlu Forests has various fruit trees, Pastures, and grasslands. The forest is scattered over an area of about 25 km2. Around a dozen endangered red deer (Cervus elaphus) live in fandoqlu Forest. These animals are under protection.
Gissoom forests
The forests are located in Gilan Province. It also has an area of about 80 hectares. Experts have identified about 76 plant species in the area. Gissoom forests are located 18 km from Talesh to Anzali Road. One end of this forest reaches the Caspian coast.
Saravan Forests
This complex is located 17 kilometers from Rasht-Tehran road in Gilan Province. There are various and rare plant species found in this area.
Alimestan Forests
This area is a district of Amol city in Mazandaran Province of Iran. It is also located 20 km from Haraz to Amol Road. Alimistan Peak is another attraction in the area. The peak is about 2,510 meters high and is suitable for hiking in winter.
Lafoor Forests
This area is part of the northern Savadkooh City in Mazandaran Province, in northern Iran. It reaches the Alborz Mountain Range on the south. Lafoor Forests have a variety of herbal plants.
Tourism Potential in Arasbaran Biosphere Reserve

According to what has been introduced above, Arasbaran has got a very high potential for tourism. Of course, with due management, tourists’ footsteps should be reduced to a minimum. If done as such, a lot can be done for nature-based tourism in the region.
Also, there is very good potential for rural tourism, agritourism, and cultural tourism in Arasbaran.