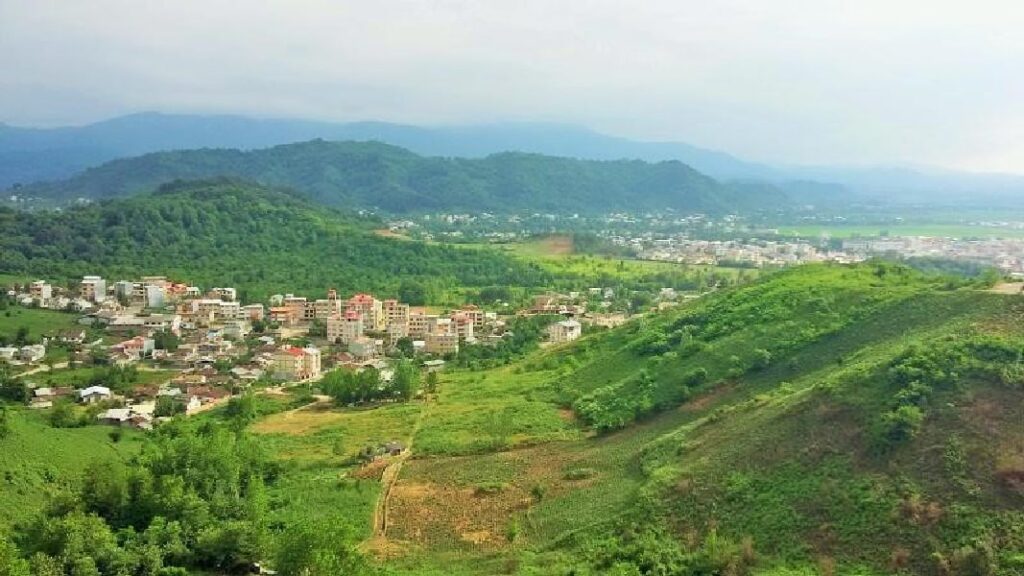
In 2019, the Hyrcanian Forests were added to the Iranian tourist attractions on the UNESCO World Heritage List. This natural attraction is located north of the Alborz mountain range and along the south coasts of the Caspian Sea. Most of the Hyrcanian forests are located in Iran and a small section is located in Azerbaijan. The Iranian section spans an area of about 55,000 km, about 7% of the total area of the country.
Locals call the forests by names such as living fossils, the center of the world, Caspian forests, and the natural museum. These forests are valuable natural resources in northern Iran.
In ancient times, “Hyrcania” was the historical administrative region including several provinces of Iran and also a part of Turkmenistan. In ancient Europe, the Greeks, and also Persians called the Caspian Sea the Hyrcanian Ocean.
The Hyrcanian forests are an 800 km long arc that extends from the northwest to the northeast of Iran. Hyrcan is derived from the old name of Gorgan City. Today, this city is the capital of Golestan province, in the southeast of the Caspian Sea. The biodiversity and authenticity of this region and its rare and unique plant and animal life attract travelers from all over Iran and the world.
This tourist attraction with its natural diversity has created an interesting variation in the social, economic, and cultural status of the region’s residents. This increases the importance of the ancient Hyrcanian forests.
History of Hyrcanian Forests
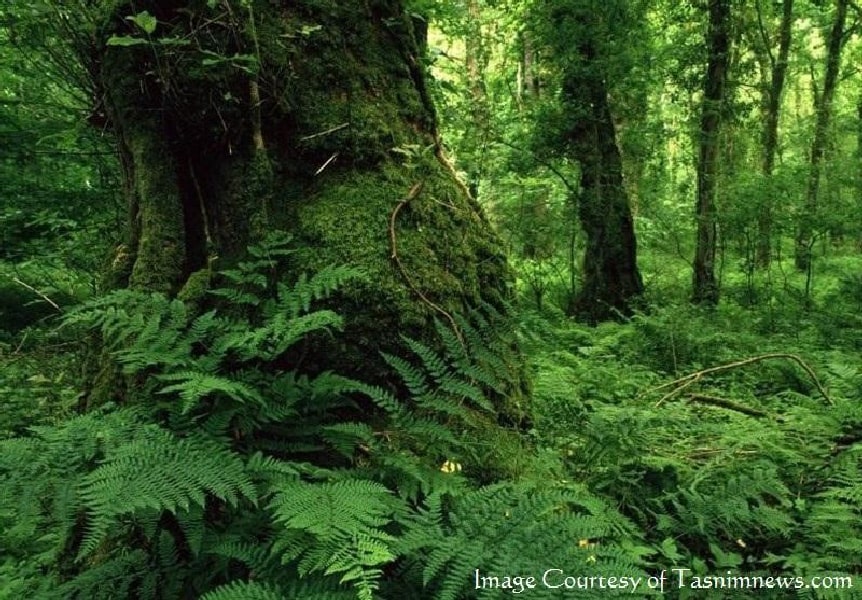

Studies indicate that the formation of these forests dates back to 25-50 million years ago, or the Cenozoic era. That means they date back to before the late Cenozoic Ice Age which started 34 million years ago. During that period, the ice age destroyed nearly all the forests in the northern hemisphere, except the Hyrcanian forests. Because Hyrcania was located between the Alborz mountain range and the Caspian Sea, a region that maintained its moderate climate. This is how these forests were saved from freezing over.
The Hyrcanian forests are the source of modern European forests. The similarity to the roots of the plants there indicates that the ice age separated the European forests from the Hyrcanian forests, but even the birds native to these forests are similar.
Geography of Hyrcanian Forests Biome
From northeast to northwest of Iran, these forests cover parts of five provinces:
- North Khorasan
- Golestan
- Mazandaran
- Gilan
- Ardabil
This natural green arc extends to the southeast of the Republic of Azerbaijan. This biome stretches to the Lenkoran Lowlands and Talish Mountains in Azerbaijan.
The Hyrcanian forests of northern Iran cover an area of 800 km long with a variable width between 20 and 70 km. The westernmost part of these forests starts from Astara in Gilan province and extends to Goli Dagi Valley in Golestan province.
Studies show that there are three climate biomes in these forests:
- Humid subtropical climate, in the medium altitudes
- Oceanic
- Humid continental, in the mountains
Forest density, slope, and distance from the Caspian Sea are some of the factors that affect the climate regions.
The maximum precipitation occurs during spring, late autumn, and winter. The average temperature in these forests is between 15 and 18 degrees Celsius. Forest soil is fertile and rich in organic and mineral substances.
Hyrcanian Forests Flora and Fauna
One of the reasons that made the Hyrcanian forests a unique natural attraction in Iran is its flora and fauna diversity. More than 3200 species of plants, 296 species of birds, and 98 species of mammals have been identified in these forests. Unfortunately, the number of these wildlife species has declined due to the environmental damage inflicted upon this ecosystem. Here we will give a brief introduction to the plant and animal species of these forests.
Vegetation
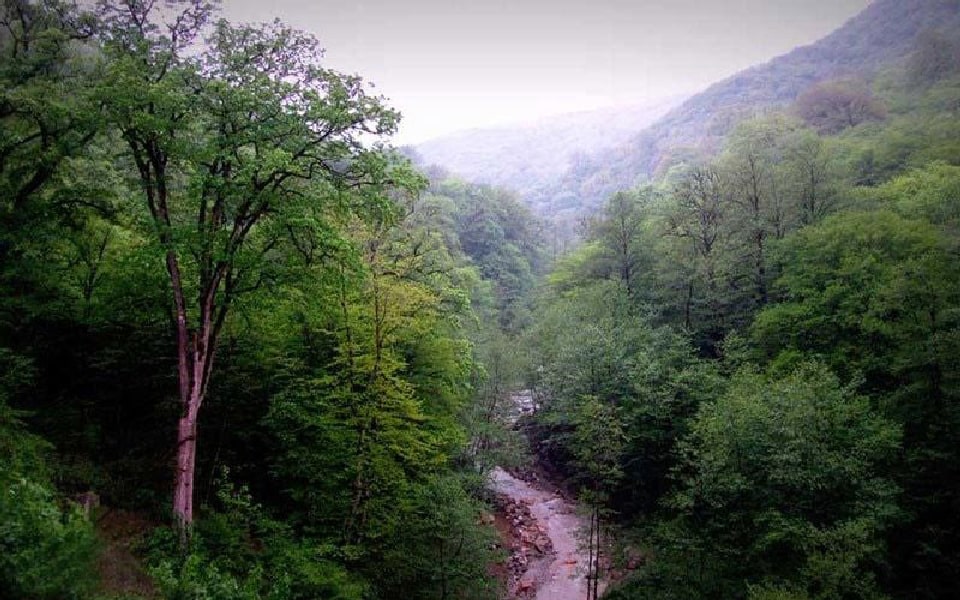

Hyrcanian forest vegetation varies based on altitude. At one time, chestnut-leaved oak (Quercus castaneifolia), Black alder, The Caucasian alder (Alnus subcordata), Caspian poplar (Populus caspica Bornm), and Caucasian walnut (Pterocarya fraxinifolia) covered the coastal flatlands of the Caspian Sea. Unfortunately, almost all of them have vanished and those forests have been converted into agricultural farms and urban areas.
The lower parts of the foothills of the Talish and Alborz mountains, with an altitude of lower than 700 meters, are covered with various subtropical forests, which include chestnut-leaved oak, Mamraz (Carpinus betulus), Persian ironwood (Parrotia persica), Caucasian Elm (Zelkova carpinifolia), Persian silk tree (Albizia julibrissin) and Date-plum (Diospyros lotus) trees.
In the medium altitudes between 700 and 1500 meters, covered with stratus clouds, the dominant tree species are hardwoods such as Oriental beech (Fagus orientalis), chestnut-leaved oak, Mamarz, Banyan fig (Ficus benghalensis) and Sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa). Chestnut-leaved oak, Banyan fig, shrubland, and Steppe, exist in Cool-summer Mediterranean climate regions and mountains.
Caspian Hyrcanian Wildlife
Some species of animals, such as the Caspian Tiger or Mazandaran Tiger (Panthera tigris tigris), once roamed these forests, but are extinct today. These forests are still home to other mammals, such as the Persian leopard, Eurasian lynx, Eurasian brown bear, wild boar, Caspian sea wolf, Golden jackal, jungle cat, Caucasian badger, and Eurasian otter, as well as certain species of birds. Steppe eagles, owls, gray ducks, vultures, and Eurasian sparrowhawks are among the birds of the region.
Protected Areas in Hyrcanian Forests
About 10% of this forest is under environmental protection, including
- Dodangeh and Chahardangeh wildlife refuge in Sari, Mazandaran
- Golestan National Park
- Central Alborz Protected Area
- Miankaleh peninsula and Lagoon in the north of Behshahr city, Mazandaran province
- Dasht-e Naz wildlife refuge in the northeast of Sari, Mazandaran province
- Siya Kashim nature preserve in the south of Anzali Lagoon in Gilan province
- Jahan Nama protected area in the southeast of Kordkuy, Golestan
- Lisar protected area in Talesh, Gilan province
- Sameskandeh Wildlife Refuge in Sari, Mazandaran Province
- Selkeh wildlife sanctuary in the Sowme’eh Sara, Gilan province
- Fandoghlu forests in Ardabil province
Deforestation
Actions such as excessive livestock grazing, soil and wood smuggling, unregulated constructions, and man-made fires have destroyed this rare biome. About 51% of the forests in this area have been destroyed.
Golestan National Park, a Protected Area in Hyrcanian Forests
The protected areas of the Hyrcanian forests possess unique characteristics and safeguard endangered animal and plant species in their refuge. Golestan National Park is the oldest protected area in Iran.
In 1957, this park was under the protection of the Hunting Club of Iran under the name of “Almeh Vaishki Protected Area”. In 1971, it was registered as the first national park of Iran on the UNESCO list under the title “Golestan Biosphere Reserve” and was introduced as one of the 50 natural reserves of the world in 1976.
This vast biome has an altitude range of about 2 thousand meters in its different parts, which has led to the formation of various microbiomes.
Golestan National Park has ample water supplies. 21 springs gurgle and several rivers flow in it. Madarsu, Zav, Qarto, Golshan Springs, Golestan, Janu, Sardarkhaneh, Dushan, Aghsu, and Karkouli are among its rivers.
The balanced synergy of mountains, forests, and abundant water supply has made Golestan Biosphere Reserve a suitable forest cover that provides a safe habitat for animals. Eurasian otter, red deer, Roe deer, wild boar, Armenian mouflon, rams, mountain goats and wild goats, Indian wolf, jungle cat, wildcat, Pallas’s cat, Indian crested porcupine, Eurasian lynx, Turkmenian fox (Persian fox) and Red fox are among the mammals found in this wildlife refuge.
But the endangered animal that increases the importance of Golestan National Park is “The Persian leopard”. The largest number of these endangered species take refuge in Golestan National Park.
In addition to the Persian leopard, other rare animals such as Red deer (Meral) and Roe deer (Shoka) also reside in Golestan National Park, which, unfortunately, is threatened by illegal hunting.
Hyrcanian Forests Tourism Potential as a Tourist Destination
For many foreign travelers, visiting this natural attraction is a great chance to see Iranian wildlife and nature. There are several routes to access this area, four main roads lead to Hyrcanian forests from Tehran. Millions of Iranians travel to that area on almost all national holidays. Throughout this area, there are resorts, hotels, and rental villas where you can stay.
If you’re visiting Iran on an Iran tour package, make sure to visit this incredible collection of ancient forests in Northern Iran. The coastline of the Caspian Sea is a popular destination for swimming, hiking in the forest, and enjoying a great variety of traditional Iranian food.
The cultural landscape of the southern region of the Caspian Sea can offer foreign travelers a chance to explore Iranian culture along with beautiful natural sights. We recommend nature tourism in Hyrcanian forests to everyone but keep in mind to follow the principles of responsible tourism.
Where is the Location of the Hyrcanian Forests?
These forests spread from the northwest to the northeast of Iran. To visit this area, first determine your destination town. You can also use the following location:
Frequently Asked Questions About Hyrcanian Forests
If you did not find the answer to your question here, leave us a comment in the comments section below this post and ask your question. We will answer it as soon as possible.
What does Hyrcan mean?
The word “Hyrkan” is derived from the word Hyrcania, the Greek pronunciation of Varkâna or Gorgan, which is the historical name for these regions.
How old are Hyrcanian forests?
These forests are 25-50 million years old. The part of these forests located in Iran remained unharmed during the Cenozoic ice age when all the forests of the world were destroyed.
What is the importance of Hyrcanian forests for the northern region?
- It is the main reason for the low pollution and great weather in the north of Iran
- These forests contain unique flora and fauna
- Preventing floods is one of the most important functions of these forests
Who owns the Hyrcanian forests?
These forests are the natural resources of Iran and are registered in the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites. In other words, they are the natural heritage of the world and should not become personal property. Therefore, no part of it should be destroyed or owned by a particular person or organization.