The history of Iran is a long and complex story of invasions, resistance, reconstructions, and the perseverance of an ancient nation.
The glory and greatness of Iranian history diminished when foreign invaders swarmed our land from all sides. Iran has experienced many ups and downs throughout its existence. It suffered devastating blows and still continued to rise. Many patriotic men and women tried to defend their country to their last breath in fateful moments and sacrificed their dear lives for Iran. People whose names are sometimes not even recorded in Iranian history books and remain anonymous.
The history of this land shows us how a nation survived its collapse after becoming a great civilization and empire. The history of Iran is a perplexing story of the conviction of a nation that has tried to preserve its identity by leaning on its cultural excellence.
In order to make it easier to remember the many dynasties of Iran’s history and easy access to a summary of Iran’s history, Destination Iran presents it in chronological order.
Chronological Order of History of Iran
The prehistoric era in Iran includes these times:
- Beyond 100,000 years ago: Lower Paleolithic Age
Stone artifacts from this period have been discovered in three provinces: Khorasan, Azerbaijan and Sistan and Baluchistan (Acheulean civilization).
- From 100,000 to 40,000 years ago: Middle Paleolithic Age
There are some artifacts dating back to this era in Iran that were discovered in several provinces, including Lorestan, Ilam, Kermanshah, Golestan, and Tehran.
- From 40,000 to 11,000 years ago: The Upper Paleolithic Age
Artifacts from this age have been found in some provinces, including Lorestan, Kermanshah, and Ilam.
- From 20,000 to 7,000 years ago: The Paleolithic era
Artifacts from this prehistoric period have been discovered in Mazandaran province.
- From 8 thousand years BC Neolithic era
The primary elements of human life in the Neolithic era consisted of gathering and storing provisions, food production, and Sedentism. The relics of this period have been found in many historical places in Iran, including hills (Tepe), and historical caves.
- From 5 thousand years BC
The historical remains of this period have been discovered in many historical sites across Iran, in hills, ancient caves, and historical rock shelters.
- From 5,000 to 4,000 years BC
This period was an era of technological advances in fields such as pottery and blacksmithing, the invention of the pottery wheel, and copper tools. The ancient artifacts from this period have been found in historical sites and hills.
- From 3 thousand years BC
Clay tablets in the early and late Elamite language have been discovered in the ruins of the ancient Gorgan civilization, and the fourth and third ancient civilizations in Giyan, Lorestan province. The artifacts from this period have been found in many historical archeological sites and historical hills.
- From 2 thousand years BC
Shagha Castle in Fars province is one of the remains of this era. The artifacts from this period have been found in many historical sites and hills across Iran.
- From 1150 to 1400 BC
This period marked the decline of the Bronze Age civilizations and the rise of Iron Age civilizations. The artifacts of this period have also been discovered in numerous archeological sites and historical hills.
History of Iran Before Islam
- From 2500 to 2600 years BC
The beginning of the rule of the Elamite dynasty, the Awan dynasty, and the war against Mesopotamia.
- From 1100 to 1450 BC
The middle Elamite period, when the war between the Elamites and Mesopotamia was still going on.
- 814 years BC Cyrus the Great, A New Civilization in Elam
Historical documents from this period were classified for 200 years.
After the war left Elam in ruins, Cyrus the Great marched there through Ashan and took control of Elam around 558 BC, opening a chapter of great empires in the history of Iran.
Ariyan Tribes Migration to the Iranian Plateau
The Medes
Several tribes united at the end of the second half of the 7th century BC, forming the Medes Empire. These peoples included the Galatians, Mauritanians, Kassites, Urartians, Caspians, and Mannaeans who united with the Ariyan tribes. Deioces founded the Medes Empire. The Assyrian civilization was defeated by the Medes. The Assyrian kingdom was considered the most ruthless force of that period.
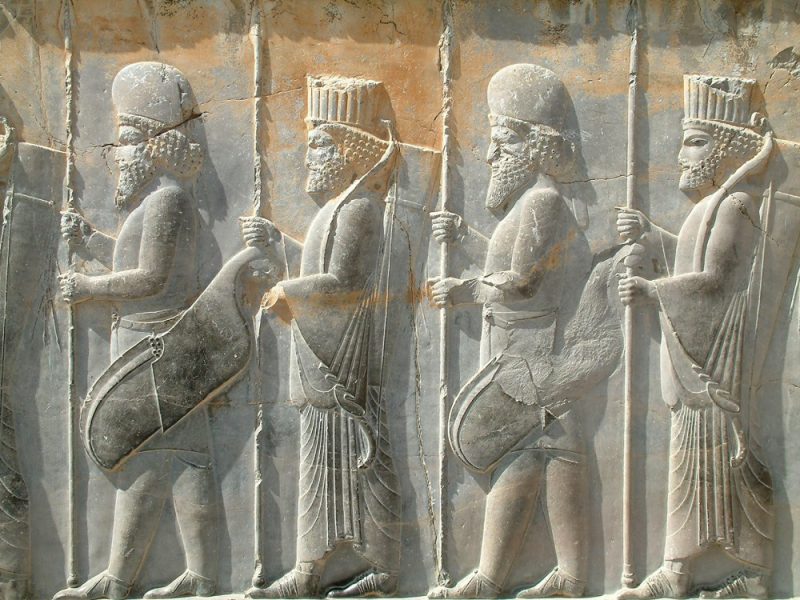
The Achaemenid
Achaemenids formed the first and largest Persian Empire in the history of Iran. Their dynasty ruled over more than a third of the world for nearly two hundred years. Cyrus II, who was rightly called Cyrus the Great, was the founder of this glorious empire. He was not only the conqueror of lands but also considered the founder of human rights in governance.
Cyrus the Great and Darius III are two influential and significant kings of the Achaemenid dynasty. The glorious Achaemenid kingdom was destroyed by Alexander the Great’s invasion of Iran, leaving but a proud memory of it in the history of Iran.
Chronology of the Achaemenid Dynasty
- 550 BC Cyrus defeated the Medes army in Pasargadae and founded the Achaemenid dynasty and began to expand his empire.
- 522 to 486 BC Darius I or Darius the Great suppressed the rebels and established the first civil society in Iran and expanded the Achaemenid empire. He ordered the construction of Persepolis.
- 330 BC Alexander the Great attacked Iran and destroyed the half-built Persepolis and took over the Persian Empire.
- 323 BC Death of Alexander.
The Seleucid
After Alexander invaded and seized Iran, his successors established the Seleucid dynasty in Iran. Alexander tried to introduce himself as a successor of Cyrus. For this reason, he married three Persian princesses against strict Greek traditions.
After Alexander’s death, his generals fought over his kingdom for twenty years until finally, Seleucus I Nicator seized the kingdom of Persia. Finally, the Seleucid dynasty was destroyed by a nomadic Parthian tribe, so that we could again witness the establishment of an Iranian empire in the history of Iran.
Chronology of the Seleucid Dynasty
- 312 to 281 BC Seleucus I Nicator established the Seleucid Greek dynasty in the land of Persia.
- 281-261 BC The rise of Antiochus I Soter and the beginning of widespread instability in Persia. After ruling for twenty years, he was killed in one of the clashes in 261 BC.
- 246 to 226 BC the rule of Seleucus II and the gradual rise of the Parthians.
- 176 to 164 BC Antiochus IV Epiphanes was the last Seleucid king. The Parthians ended the rule of the Seleucids in Iran.
The Parthians
The Parthians were a tribe from Parthia in the northeast of Greater Iran. They were brave nomadic people who had considerable military might and were able to drive the Seleucid forces away from Persia and establish the rule of the Parthians. They named this dynasty after their ancestor Arsaces I, known as the Ashkanian Dynasty.
Chronology of the Parthian Dynasty
- 250 years BC The Parthian Empire conquered Khorasan, then this city came under the control of the Seleucids.
- 161 to 138 years BC Mehrdad I or Mithridates I of Parthia expanded the Parthian Empire.
- 123 to 89 BC Mehrdad II or Mithridates II of Parthia was the king of Iran. He made a peace treaty with General Lucius Cornelius “Sulla” Felix, the envoy of Rome, and drove back the invading Scythian tribes from Iran. Mehrdad II annexed Armenia and a large part of Mesopotamia to Iran.
- 123 BC to 87 BC The peak of the Parthian Empire.
- From 87 BC to 224 BC The decline of the Parthian Empire and the rise of the Roman Empire. During this period, conflict over power and fratricide became common among the Parthians and resulted in the weakness of the Parthian dynasty.
- 224 AD Ardavan V or Artabanus IV of Parthia was defeated by Ardeshir I, founder of the Sassanid dynasty, and was killed by him. The Parthian dynasty ended with the death of Artabanus V.
The Sassanid
After the Parthians, the Sassanid dynasty assumed control of Iran. During their time, Zoroastrianism and Zoroastrian Mobads (Magi) were highly influential, and fire temples prospered for the first time in the history of Iran. Different social classes were formed in society. The Sassanid kings, who held the highest social rank, believed they were blessed with Khvarenah or divine royal glory. The Sassanid government was destroyed by the Arab invasion of Iran.
Chronology of the Sasanian Dynasty
- 224 AD to 241 AD Ardeshir I or Artaxerxes I defeated the Parthians and founded the Sassanian Empire.
- 241-272 AD Shapur I invaded the Roman Empire (252-261 AD) and captured Emperor Valerian in 260 AD.
- 242 AD to 273 AD Popularity of Mani, Founder of Manichaeism,
- 250 AD to 300 AD Armenia’s religion changed to Christianity.
- 283 AD Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius Carus captured Ctesiphon. Armenia and northern Mesopotamia were surrendered to Rome.
- 363 AD Shapur II defeated Julian the Apostate in battle and conquered Armenia and northern Mesopotamia.
- 379 AD Peace treaty between Sassanid and Roman Empires.
- 425 AD Hephthalites attacked Khorasan.
- 489 AD Church of the East was built in Mesopotamia.
- 499 AD to 531 AD Pinnacle of Sassanid Empire.
- 529 AD Justinian the Great closed the schools. Scholars migrated to Iran from Byzantine.
- 608 AD The Sassanid Siege of Byzantium.
- 614 AD Khosrow II conquered Damascus and Jerusalem and brought The True Cross to Ctesiphon.
- 622 AD Heraclius defeated Khosrow II. Prophet Muhammad, the Prophet of Islam, left Mecca for Medina.
- 632 AD death of Prophet Muhammad.
- 632 to 651 AD Yazdegerd III, the last Sassanid king came to power.
- 635 to 641 AD Arabs conquered Damascus and Ctesiphon. They defeated the Persians and annexed Persia to the Arab Empire.
- 651 AD death of Yazdegerd III.
The History of Iran After Islam
Public discontent with Sassanid’s authority gave the Arabs invaders ample opportunity to attack and conquer Iran. After the collapse of the Sassanid kingdom and the Arab conquest of Persia, a new chapter opened in the history of Iran, marking the beginning of the Islamic history of Iran.
After the Arab invasion of Iran, Iranians experienced three periods of Arab rule: The Rashidun Caliphate, the Umayyad Dynasty, and the Abbasid Caliphate. All of them were faced with the unrest and rebellion of Iranians against Arab rule. Since the Abbasid caliphate, Iranians gradually managed to establish semi-independent local governments, leading to the decline of the Caliphate’s rule over Iran.
Iranian History After the Arab Invasion of Iran
- 661 to 750 AD The rule of Umayyad Caliphate in Damascus.
- 750 to 1257 AD The rule of the Abbasid Caliphate in Baghdad.
- 756 to 1031 AD Arab Caliphate of Córdoba.
- 872 to 903 AD The establishment of the Saffarid dynasty in Khorasan.
- 903 to 999 AD The rise of the Samanid dynasty in Khorasan.
- 935 to 1055 AD The rise of the Buyid dynasty near Shiraz.
- 962 to 1044 AD The emergence of the Ghaznavids dynasty in the east and challenge to Samanid authority.
Seljuk and Ilkhanid (Mongol)
From 1037 until 1055 AD, the Seljuk Turks attacked Iran led by Tughril I. The Buyid dynasty was ended by Abu Muslim Abd al-Rahman ibn Muslim al-Khurasani, the Iranian commander of the Abbasid Revolution.
Chronology of Seljuk and Ilkhanid Periods
- 1073 AD The pinnacle of Seljuk dynasty.
- 1090 AD to 1257 AD The establishment of Al Ismail, or Nizari Ismaili state
- who were later called “Hashashins” or assassins, in the Alamut region, the southern foothills of the central Alborz mountain range ad near Qazvin.
- 1117 AD to 1157 AD Reign of Sultan Ahmad Sanjar and the end of the Seljuk dynasty in Iran.
- 1219 AD to 1227 AD Near total destruction of Iran by the Moghul invasion of Genghis Khan.
- 1256 AD to 1265 AD Establishment of Ilkhanid dynasty by Hulagu Khan, Genghis Khan’s grandson, and appointment of Maragheh as capital.
- 1295 AD to 1304 AD Ghazan Khan and his eventual conversion to Islam.
- 1334 AD The end of the Ilkhanid dynasty.
Timurid
Chronology of Timurid Dynasty
- 1380 AD to 1393 AD Timur conquered Iran. The Church of the East was closed.
- 1397 to 1447 AD Timur destroyed India and died shortly after. His successor, Shahrukh Mirza, conquered the “Amu Darya” region.
- 1408 AD to 1453 AD Rise of Qara Qoyunlu Turkmen.
- 1461 AD The Ottoman Turks invaded the northwest of Iran and pushed the Timurids back to the east.
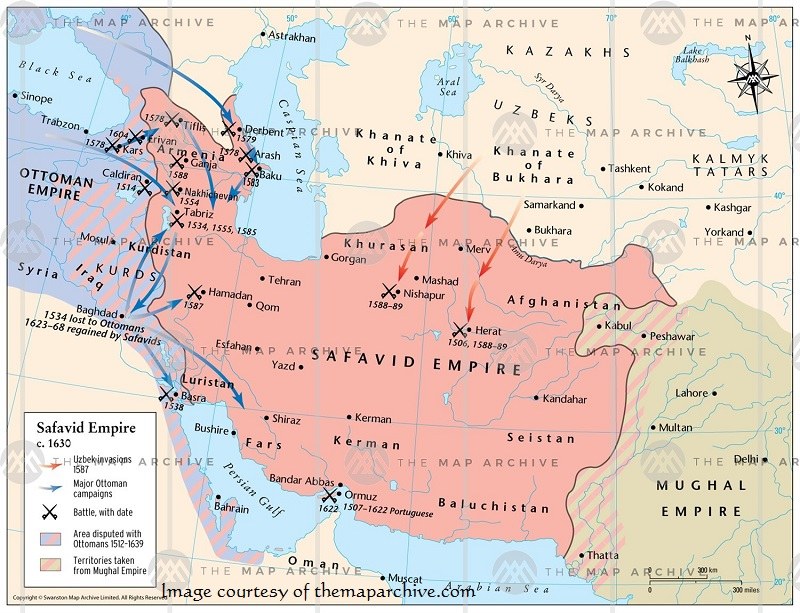
Safavid
The Safavid were able to establish a powerful central government in Iran. Shah Ismail is the founder of this dynasty. Shah Abbas led this dynasty to the peak of power and stability.
During the Safavid era, Iran was engaged in constant conflict with the Ottoman Empire, its neighbor to the east.
Chronology of Safavid Dynasty
- 1502 AD to 1524 AD Shah Ismail I founded the Safavid dynasty. Shia Islam was declared the country’s official religion for the first time in the history of Iran.
- 1587 AD to 1628 AD Shah Abbas I defeated the Ottomans in the north, conquered Baghdad, and selected Isfahan as the capital.
- 1624 AD to 1722 AD The Afghan Siege of Isfahan led to the ransacking of the kingdom. The Safavid dynasty was dethroned. At this time, Soltan Hoseyn was the king. After him, Shah Tahmasab II and Shah Abbas III tried to seize power in some regions of Iran but were unsuccessful.
- 1722 AD to 1724 AD The Afghan army conquered Iran and pillaged Isfahan and Shiraz. They massacred the Safavid princes.
Afsharid and Zand
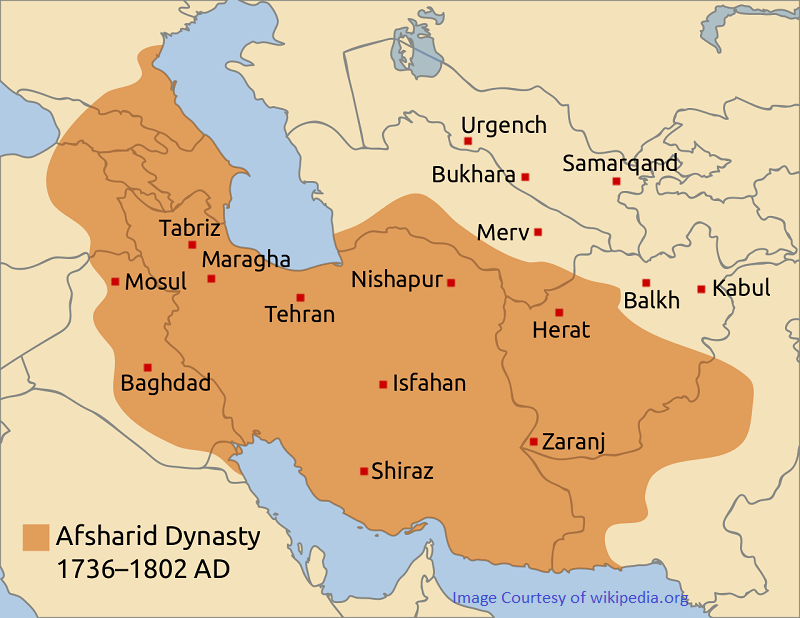
Nader Qoli was a war general who freed Isfahan from the Afghan invaders and delivered it to the Safavid king, Shah Tahmasab II. Shah Tahmasp was defeated in the battle with the Ottomans and signed a peace treaty with the Ottoman Empire. Nader Qoli Khan realized the Safavid incompetence and decided to take matters into his own hands.
With the support of Iranian elders, Nader Khan was crowned Nader Shah and founded the Afsharid dynasty. After Nader Shah Afshar, the Afshar dynasty did not have a powerful king and was replaced by the Zand dynasty.
Chronology of the Afsharid and Zand Dynasty
- 1729 AD to 1739 AD Nader Qoli Khan established the Afsharid dynasty, drove out the Afghan invading forces, and conquered Afghanistan and India. Then he repelled the Ottoman invasion of Iran. He did not have a proper successor and with his death, the Afsharid dynasty collapsed.
- 1750 to 1795 AD The Zand dynasty ruled with Shiraz as Capital. After the Afsharid and before the rise of the Qajar in Iran, Karim Khan Zand established a government in Iran that lasted 46 years.
The Qajar
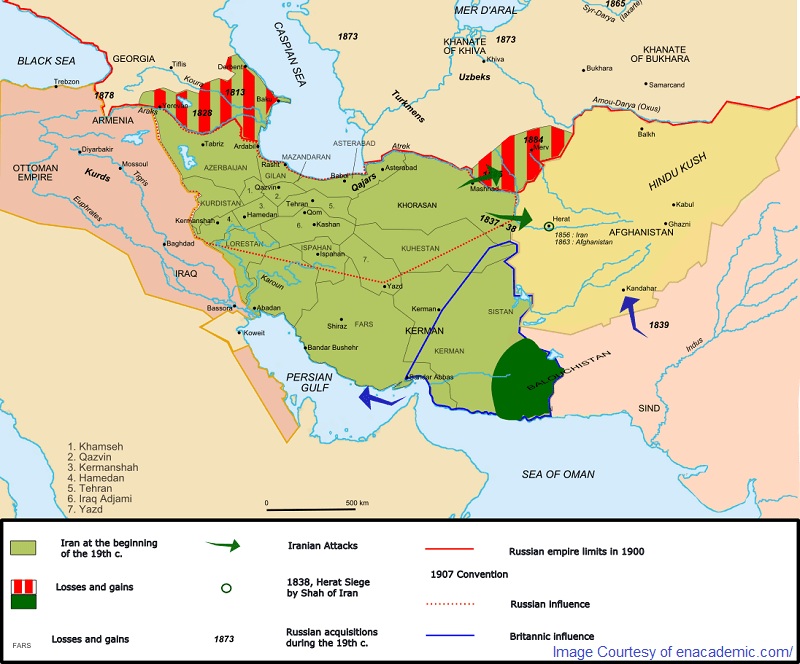
The Qajar dynasty ruled Iran for 130 years. During their reign, important regions of Iran were lost to foreign interests, and the country encountered a rather eventful period.
Chronology of Qajar Dynasty
- 1795 AD to 1925 AD The Qajar dynasty was a local authority and ruled in Tehran.
- 1796 AD Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar founded the Qajar dynasty.
- 1818 AD During the reign of Fath-Ali Shah Qajar, the Treaty of Gulistan was finalized between Iran and Russia, which saw lands from the north of Iran surrendered to Russia.
- 1827 AD Russian Occupation of Tabriz.
- 1828 AD The Treaty of Turkmenchay was signed between Fath-Ali Shah Qajar and the Tsarist government of Russia, concluding the Russia-Iran war. According to this agreement, Yerevan, Nakhichevan, and the remainder of Talysh Khanate were surrendered to Russia.
- 1896 to 1906 AD Persian Constitutional Revolution took place.
- 1906 AD Establishment of Persian Parliament, Constitutionalism was officially adopted as a system of government.
- 1908 AD Rise of Iranian Nationalist Movement.
- 1909 AD The Anglo-Persian Oil Company was founded; This company was later called British Petroleum.
- 1917 to 1919 AD The Persian famine occurred in Iran during the First World War. 40% of Iran’s population perished in this famine.
- 1920 AD The uprising of Shaikh Mohammad Khiābāni in Tabriz and Mirza Kuchik Khan in Gilan.
- 1909 AD to 1923 AD Ahmad Shah was the last Qajar king. Reza Khan was appointed as the Prime Minister.
- 1922 AD The 1921 Persian coup d’état by Reza Khan and the removal of Ahmad Shah, the last Qajar king. The Qajar dynasty collapsed in 1924.
Pahlavi
With the collapse of the Qajar dynasty, the Pahlavi dynasty gained power in Iran. During this period, Iran entered a new era of development and took a step toward modernity. The history of Iran witnessed the modernization of the country for the first time. Reza Shah Pahlavi tried to revive the ancient culture of Iran and the ancient Persian empire. He is known for his dominance and dictatorship in governance.
Chronology of the Pahlavi Dynasty
- 1925 AD Reza Khan declared himself “Reza Shah” and founded the Pahlavi dynasty.
- 1314 AD The title of Pars or Persia was selected for Iran and globally announced as the official name of the country.
- 1941 AD During World War II, the Allies occupied Iran. Reza Shah abdicated the throne and went into exile. His son Mohammad Reza replaced him as the next Pahlavi king.
- 1943 AD The Tehran Conference was held hosting Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin. Iran regained its territorial integrity.
- 1951 AD Dr. Mohammad Mosaddegh was elected as the prime minister and worked towards the nationalization of the oil industry.
- 1953 AD The 1953 Iranian coup d’état against the Nationalization of the Iranian oil industry, during which Mohammad Mosaddegh was arrested and put on trial. Mohammadreza Shah returned to Iran.
- 1955 AD Iran joined the Central Treaty Organization.
- 1959 AD Iran signed a defense pact with the United States.
- 1963 AD Ayatollah Khomeini instigated a religious uprising on a national level and in protest against the Shah.
- 1967 AD Official Coronation of Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi and Queen Farah Pahlavi.
- 1969 AD Heightened tensions between Iran and Iraq over the rights to Arvandrud (Shatt Al Arab).
- 1971 AD The 2,500-year celebration of the Persian Empire.
- 1978 to 1979 AD People’s protests against the monarchy increased, and Mohammadreza Shah left Iran, leading to the collapse of the Pahlavi dynasty.
The Islamic Republic of Iran
Chronology of the Islamic Republic of Iran
- 1979 AD The majority of Iranians voted to establish the government of the Islamic Republic of Iran under the leadership of Ayatollah Khomeini.
- 1980 AD Iraq Invasion of Iran and Iran–Iraq War.
- 1988 AD Iran and Iraq recognized United Nations Security Council Resolution 598 and Iran announced the final ceasefire of the 8-year war.
- 1989 AD Ayatollah Khomeini died and Ayatollah Khamenei was selected as the Supreme Leader of the Islamic Republic.
Summary Table of Iranian History
Here is a brief table indication the history of Iran at a glance:
| Row | Dynasty | Start | End |
| 1 | Medes | 549 BC | 607 BC |
| 2 | Achaemenid | 330 BC | 550 BC |
| 3 | Seleucid | 247 BC | 330 BC |
| 4 | Parthian | 224 BC | 247 AD |
| 5 | Sassanid | 224 AD | 642 AD |
| 6 | Arab Rule | 642 | 821 |
| 7 | Tahirid | 821 | 893 |
| 8 | Alid | 828 | Gradual Collapse |
| 9 | Saffarid | 867 | 892 |
| 10 | Samanid | 892 | 1005 |
| 11 | Zyarid, Buyid and Daylamites | 928 | 1052 |
| 12 | Ghaznavids | 962 | 1040 |
| 13 | Seljuk | 1040 | 1256 |
| 14 | Khwarazmian or Anushtegin | 1194 | 1231 |
| 15 | Ilkhanid | 1256 | 1383 |
| 16 | Timurid | 1383 | 1501 |
| 17 | Safavid | 1501 | 1736 |
| 18 | Afsharid and Zand | 1736 | 1795 |
| 19 | Qajar | 1795 | 1925 |
| 20 | Pahlavi | 1925 | 1979 |
Learn More About the History of Iran
- Investigating the rise and fall of the Achaemenids by visiting three historical places
- Iran on the ancient silk road, the old network of trade routes
- History of Khwarazmian; The era of fear and war (1077 to 1231 AD)
- History of Ghaznavids in Iran after Islam (977 to 1186 AD)
- History of Zyarid, Buyid, and Daylamites (928 to 1062 AD)
- History of Samanid in Iran after Islam (819 to 999 AD)
- History of Saffarid in Iran after Islam (861 to 1003 AD)
- History of Alid in Iran after Islam (year 863 to 928 AD)
- The history of Tahirid in Iran after Islam (from 821 to 873 AD)
- The Importance of Cyrus the Great in the History of Iran
Frequently Asked Questions About the History of Iran
If you cannot find the answer to your question about the history of Iran here, leave us a comment in the comments section below this post and ask your question. We will answer it as soon as possible.
What are the major prehistoric civilizations of Iran?
In the history of Iran, there have been various ancient civilizations, some of which were independent states and some semi-autonomous. The most important of these civilizations are:
● Shahr-e Sukhteh Ancient Civilization (burnt city) in Sistan
● Shahdad Kalouts in Kerman
● Tepe Sialk in Kashan
● Marlik Hill civilization in Gilan
● Jiroft Culture in Kerman
● Elam civilization in Khuzestan
● Teppe Hasanlu civilization in Azerbaijan
How old is civilization in Iran?
By examining the oldest discovered artifacts of ancient settlements in Iran, such as Tepe Sialk and Savojbolagh ills, we can trace back Iranian ancient civilizations to before 7500 BC.
What is the prehistoric period?
The prehistoric period or the prehistoric era refers to a time when humans did not yet have the capacity or tools to record history or leave behind any traces of their civilization. One of the most important reasons for this is the fact that writing systems were not invented. Historians can only make assumptions about their way of life and the condition of the people based on the remaining evidence from that era.
What are the different prehistoric periods in the history of Iran?
In general, the Iranian prehistoric era is divided into four parts:
The Paleolithic and Epipalaeolithic age (from about one million years to roughly 12 thousand years ago)
The Neolithic period (from about 10 thousand to 8 thousand years ago)
The Chalcolithic Age (from about 8 thousand to 5300 years ago)
The Bronze Age (from about 5300 to about 4000 years ago).
Are all Iranians ethnically Aryans?
There is no such thing as a pure ethnic group in the world. Aryan tribes entered Iran in the second millennium BC and integrated with other tribes in the Iranian plateau. Therefore, Iranians cannot be considered Aryans.
In addition, some experts have recently claimed that the great Aryan migration to the Iranian plateau did not happen. Rather, various tribes and races that we consider Aryans have always lived on this plateau. They were the ones who migrated to some of the northern regions of Greater Iran and also to Europe.
What was the ancient name for Iran?
The ancient name for Iran was Pars or Persia. The word Iran is also mentioned in ancient Avesta texts. Iran was the name that grew popular in the first Pahlavi period.
Are all Iranians Persian?
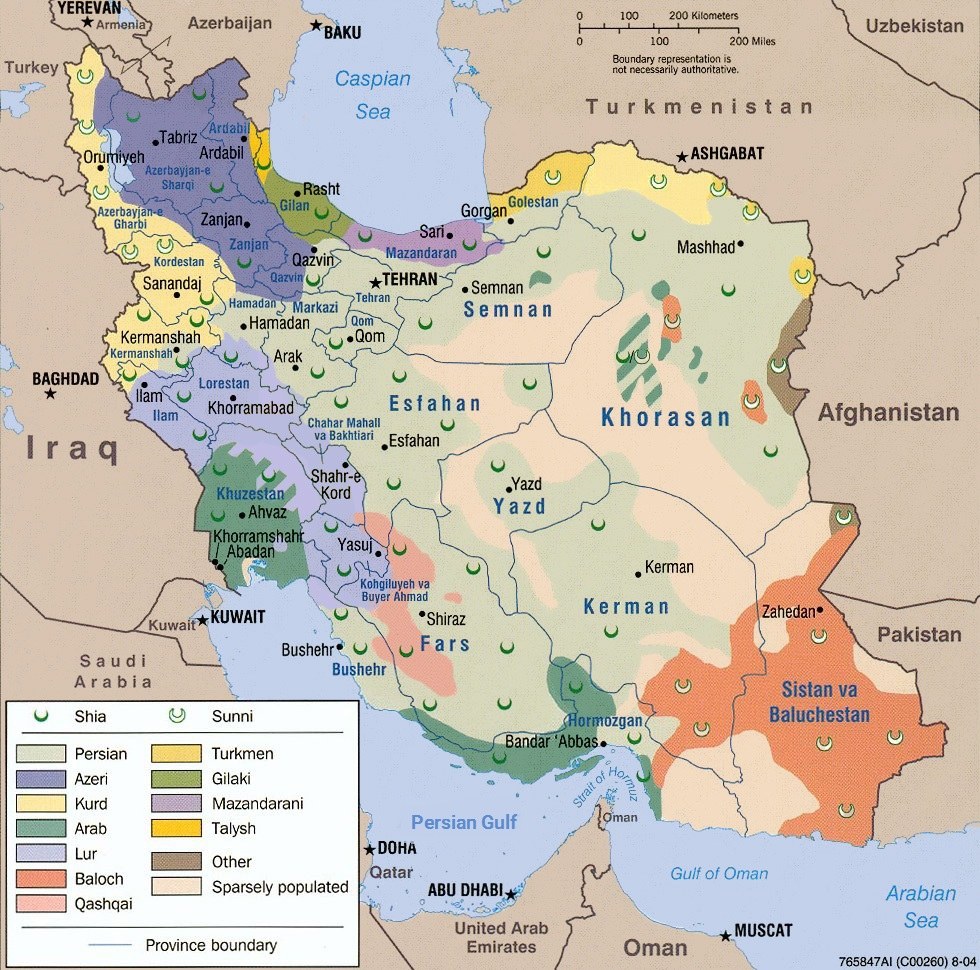
The Iranian nation consists of different Persian, Kurdish, Baluch, Gilaki, Arab, Lor, and Azari ethnic groups. Parsians or Parthians are also one of the Iranian tribes.
What role have Iranians played in the development of human civilization?
Iranians have played an ancient and important role in the evolution of the ancient civilizations of the world, and they have been practicing Sedentism since the 6th millennium BC.
When does the history of ancient Iran begin?
Historians consider the period from the rise of the Medes Empire (549 BC) to the collapse of the Sassanid dynasty and the Arab invasion of Iran (632 AD) the history of ancient Iran.
How old is the history of Iranian civilization?
According to archaeological findings and evidence, ancient civilizations emerged on the Iranian plateau more than seven thousand years ago. Some consider the establishment of central governments in Iran as the beginning of Iranian history and believe that Iran as a nation formed with the beginning of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC.
In general, experts believe that Iran is more than 7 thousand years old.
Was Iran a larger country in ancient times?
The biggest empires in the world have been established in or governed from Iran: The Achaemenid, Sassanid, Seljuk, and Ilkhanid empires.
Who was the founder of the first central government in Iran?
Cyrus the Great founded the Achaemenid Empire in 550 BC. The history of Iran couldn’t start without his ambitious efforts.
How old are the most ancient relics found in Iran?
The oldest man-made artifacts found in Iran date back to 200,000 years ago, which were made of stone.
How old are the most ancient architectural structures discovered in Iran?
Since 8,000 years ago, Iranians have been building houses in hills in the historic Savojbolagh region and Tepe Sialk and Harsin hills.
How many historical hills are located in Iran?
It is estimated that Iran has 200,000 historical hills belonging to different prehistoric and historical eras.
How many powerful dynasties were in Iran before Islam?
The largest territory and the most powerful kingdom in the history of Iran before Islam was the Achaemenid government. Of course, the Sassanid also gained huge influence and power at some junctures in Iran’s history before Islam.
How long was Iran under the control of Arabs after the arrival of Islam?
The Arabs invaded Iran in 633 AD and caused the collapse of the Sassanid dynasty. This control lasted until 821 AD when the Tahirid established a semi-autonomous government.
When did the Islamic historical era in Iran begin?
In the history of Iran, the Islamic period begins with the fall of the Sassanid empire and the victory of the Arabs. The Arab conquest of Persia brought about major changes in various aspects, including social, religious, and political. For this reason, many experts use the term “Islamic Period” to describe Iranian history after Islam.
What were the major wars that took place in ancient ran?
The Battle of the Persian Gate between Iran and the Greeks in 330 BC and the Roman–Persian Battle of Emesa in 272 AD were two major battles in ancient Iran.
How many times has Iran been invaded throughout history?
● Alexander’s conquest of Persia: 334 BC
● Roman Invasion of Persia: 283 AD
● The attack of the Seljuk Turks: 1037 AD
● Mongol invasion of the Khwarazmian Empire: 1219 AD
● Timur’s military conquest of Persia: 1383 AD
● Afghan invasion of Isfahan: 1722 AD
● Ottoman Siege of Trebizond: 1461 AD
● Russian invasion: 1827 AD
● Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran: 1941 AD
● Iraqi Invasion: 1980 AD